The MoEDAL-MAPP Experiment
In 2010 the MoEDAL experiment at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) was unanimously approved by CERN's Research Board to start data taking in 2015 and reapproved for Run-3 in 2021. MoEDAL is a pioneering experiment designed to search for highly ionizing avatars of new physics such as magnetic monopoles or massive (pseudo-)stable charged particles. Its groundbreaking physics program defines over 30 scenarios that yield potentially revolutionary insights into such foundational questions as: are there extra dimensions or new symmetries; what is the mechanism for the generation of mass; does magnetic charge exist; what is the nature of dark matter; and, how did the big-bang develop. MoEDAL's purpose is to meet such far-reaching challenges at the frontier of the field.
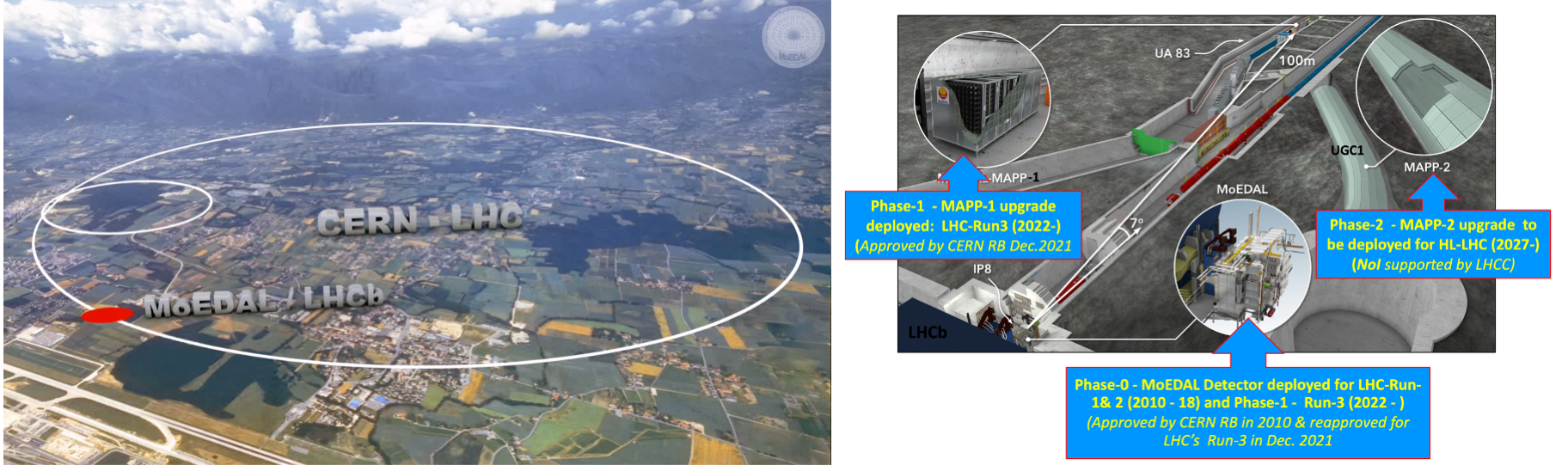

The innovative MoEDAL-MAPP detector employs unconventional methodologies tuned to the prospect of discovery physics. The largely passive MoEDAL detector, deployed at Point 8 on the LHC ring, has a dual nature. First, it acts like a giant camera, comprised of nuclear track detectors - analyzed offline by ultra fast scanning microscopes - sensitive only to new physics. It does not require electronic readout or a trigger. Second, it is uniquely able to provide a permanent record of new physics and trap the particle messengers of physics beyond the Standard Model for further study. MoEDAL's radiation environment is monitored by a state-of-the-art real-time TimePix pixel detector array. The MoEDAL detector will take data in Run-3 with: improved detector efficiency; ten times lower charge threshold, 50e to 5e, where e is the unit electric charge; 5 times greater instantaneous luminosity; and, the higher collision energy of 14 TeV.
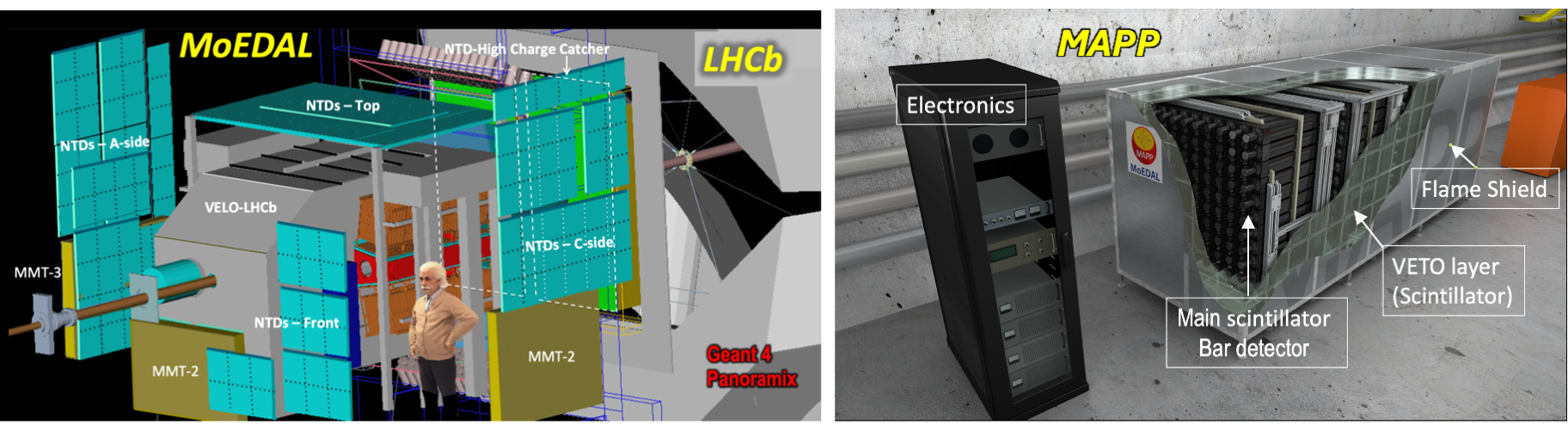
The new MAPP detector is a state-of the art scintillator detector designed to search for Feebly Interacting Particles (FIPs), such as Milli-Charged Particles (mCPs), with charge as small as of the order of thousandth the electron charge. MAPP also has sensitivity to charged and neutral LLPs. The MAPP detectors represents a “Phase-1” addition to the MoEDAL program for Run-3. A 3D computer model of the MAPP-1 detector - deployed in the UA83 tunnel situated 110m underground and 100m from IP8 at an angle of 7 deg. to the beam - is shown in the Figure above. Unlike MoEDAL, MAPP is an active detector with electronic-readout and a software/firmware trigger.
